TAO
TAO is a distributed datastore serving with API tailored for social graph.
Background
Facebook original used Mysql + lookaside cache(memcache), and encountered below issues when dealing with social data model:
- Inefficient edge lists: kv cache always require to fetch entire edge lists and change a sing edge require the entire list to be reloaded
- Distributed control logic: control logic is run on clients that don’t communicate with each other
- Expensife read-after-write consistency: async Master/Slave mysql replica
TAO suits for social graph model with much higher read than write
Data model and API
A typical social graph model:

Objects and Associations
There are two data types in TAO: 1) Objects, typed nodes 2) Associations, typed directed edges
Object: (id) -> (otype, (key -> value)*)
Assoc: (id1, atype, id2) -> (time, (key -> value)*)Associations naturally model actions that can happen at most once or record state transitions, such as the acceptance of an event invitation, while repeatable actions are better represented as objects.
TAO provides simple api to crud Objects and Assoc
Association query API
TAO’s assoc query api mostly built to get assoc list:
Association List: (id1, atype) -> [a_new...a_old]- assoc_get(id1, atype, id2set, high?, low?)
- assoc_count(id1, atype)
- assoc_range(id1, atype, pos, limit)
- assoc time range(id1, atype, high, low, limit)
Architecture
Storage Layer
- TAO can be built on top of any database. Facebook is using MySQL as storage layer.
- MySQL server is divided into logical shards belongs to logical databases.
- By default, object and assoc are stored in two different tables, and objects are bound to a shard for the life time with association stored on the shard of its id1.
Caching Layer
- TAO’s caching layer implements the API for clients and handling all the communications with database (cache miss and write requests).
- Multiple cache servers constitute a tier and tier is in charge of responding to any request.
- Write operation of association will write to two shards with inverse edge, and if failure happens, it’ll be fixed by an asynchronous job
Leaders and followers
- TAO has a leader tier and multiple follower tiers
- Leader acts as single cache coordinator to database, reading from and writing to the storage layer
- Followers forward cache misses and writes to a leader
- TAO provides eventual consistency by asynchronously syncing maintenance message between leader and followers
- an object update in the leader will send update message to followers
- all messages contain version number so followers can ignore late arrived update
- Since TAO only cache contiguous prefixes of association list, association update is expensive (it’ll truncate the list and disregard many edges), TAO used refill instead of update
- Association update in leader
- Leader sends refill message to followers holding association
- Follower trigger a query to leader to update the association list
- Leader can serialize concurrent writes and control the traffic to avoid thunder herding database
Scaling geographically
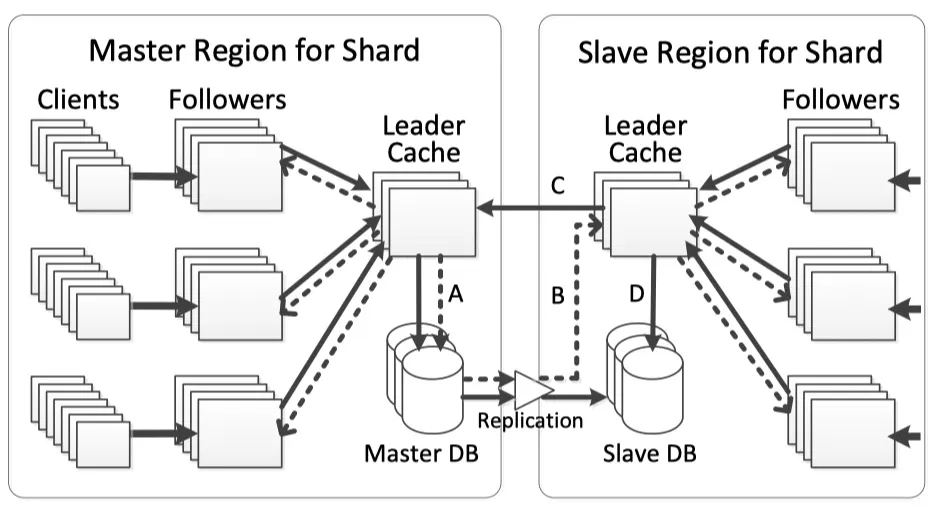
- In Facebook production environment, followers, leaders and databases may be located thousands of miles apart and the network round trip is slow
- Facebook used a Master/Slave architecture as showed in the picture
- The master region sends read misses, writes, and embedded consistency messages to the master database (A).
- Consistency messages are delivered to the slave leader (B) as the replication stream updates the slave database.
- Slave leader sends writes to the master leader (C) and read misses to the replica DB (D).
- TAO embeds invalidation and refill messages in the database replication stream.
- Leader will update a forwarded write even before database being updated (B)
Consistency and Fault Tolerance
Consistency
- TAO guarantees eventual consistency after a write update via refile or invalidation
- TAO provides read-after-write within a single tier.
- There’s a rare race condition case, when it takes longer for the slave region’s storage server to receive an update than it does for a cached item to be evicted from cache
Failure Detection and Handling
- Database failure:
- master is down: one of slave will be automatically promoted to master
- slave is down: redirect traffic to master
- Leader failure:
- read miss will reroute to db
- write will be rerouted to a random member of the leader’s tier and replacement leader will enqueue invalidation asynchronously to original leader once it’s back
- Refill and invalidation failure:
- follower un-reachable: leader will store updates and invalidation to disk system and will send later
- leader failure: new leader will invalidate all of shards mapped to original leader to restore consitency
- Follower failure: reroute to followers in other tiers